The FAO Meat Price Index averaged 127.8 points in September, up 0.9 points (0.7%) from its revised August level and 7.9 points (6.6%) from the same period last year, reaching a new all-time high.
Beef prices climbed to unprecedented levels, primarily supported by strong demand in the United States, where limited domestic supplies and favorable price differentials continue to stimulate imports, particularly from Australia, where prices have risen. Brazilian beef prices rose in tandem with strong global demand, offsetting the impact of reduced export channels to the United States due to increased US tariffs.
Global sheepmeat quotations rose sharply due to strong import demand, while export supplies from Oceania were limited.
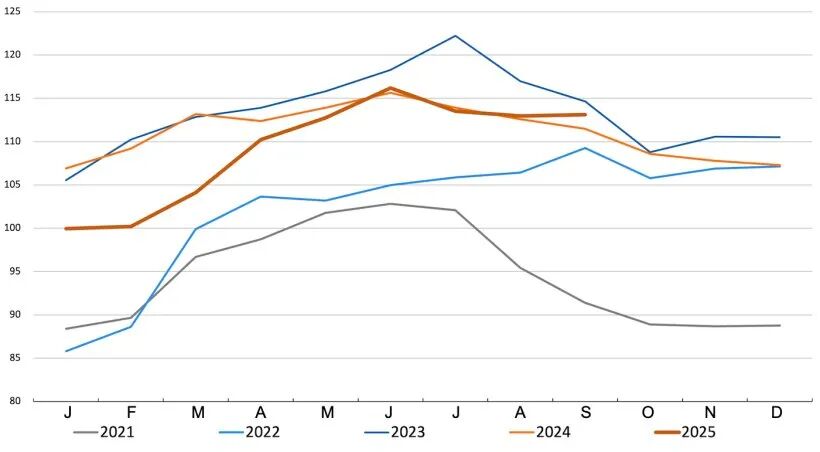
Global pork prices remained stable as strong demand for Brazilian pork in alternative markets offset reduced Chinese purchases. In the European Union, pork export prices fluctuated slightly. Poultry prices remained firm, reflecting a relatively balanced global market despite ongoing import restrictions related to localized outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian influenza.
Beef prices climbed to unprecedented levels, primarily supported by strong demand in the United States, where limited domestic supplies and favorable price differentials continue to stimulate imports, particularly from Australia, where prices have risen. Brazilian beef prices rose in tandem with strong global demand, offsetting the impact of reduced export channels to the United States due to increased US tariffs.
Global sheepmeat quotations rose sharply due to strong import demand, while export supplies from Oceania were limited.

Global Pork Price Index
Global pork prices remained stable as strong demand for Brazilian pork in alternative markets offset reduced Chinese purchases. In the European Union, pork export prices fluctuated slightly. Poultry prices remained firm, reflecting a relatively balanced global market despite ongoing import restrictions related to localized outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian influenza.

